Taking huge risks in finance may seem like a bad idea for most people. But, sometimes there is more to gain if you are willing to act a bit dangerously. So we are going to see all about market risks and market risk premiums. We will also get to know the different types. We will learn to calculate market risk premium using the formula and calculator. In addition, we will be able to look at market risks in banking and how to manage them. All these will help us to make better risks.
What are Market Risks?
The term Market risks refer to the risk that an investment may face due to fluctuations in the market. It covers all the risks of financial loss resulting from changes in market prices. The risk is that the venture’s value will reduce. Also known as systematic risk, the term may also refer to a specific currency or product.
We cannot only link Systematic risk with the company or the industry one is investing in; rather, it depends on the performance of the entire market. We show it generally in yearly terms, either as a fraction of the first value (e.g. 6%) or an absolute number (e.g. $6).
Systematic risk contrasts with specific risk, also known as business risk or unsystematic risk. It is tied directly with a market sector or the performance of a particular company. In other words, it refers to the total economy or securities markets, while specific risk involves only a part.
Thus, it is necessary for an investor to keep an eye on various small variables related to the commercial market. They include inflation, interest rates, the balance of payments situation, financial debts, geopolitical factors, etc.
Types of Market Risks
#1. Interest Rate Risk
This is the risk that comes from a rise or drop in interest rates. The risk arises from unanticipated changes in the interest rates due to monetary policy measures taken by the central bank.
#2. Commodity Risk
Certain goods, such as oil or food grain, are important for any economy and assist the production process of many goods. This is due to their use as secondary inputs. Any change in the prices of these products generally affects the performance of the entire market. It often results in a demand crisis.
#3. Currency Risk
Currency risk is also known as exchange rate risk. It refers to the possibility that foreign exchange rates will go up or down. We usually take the risk into study when making an international investment.
In order to decrease the risk of losing out on foreign investment, many rising markets maintain high foreign exchange reserves. Thus, ensuring that any possible loss can be canceled by selling the reserves.
#4. Country Risk
Many small variables, outside the control of a financial market, can affect the level of return due to an investment. They include the level of political balance, level of financial debt, prone to natural disasters, ease of doing business, etc. The degree of risk associated with such factors must be taken into consideration while making an international investment decision.
#5. Equity Risk
This is the risk that share prices will change. It is the financial risk involved in holding equity in a particular investment. Equity risk often refers to equity in companies through the purchase of stocks. It doesn’t commonly refer to the risk in paying into real estate or building assets in properties.
#6. Inflation Risk
Inflation risk is the chance that the cash flows from an investment won’t be worth as much in the future. This is a result of changes in purchasing power due to inflation. Another name for inflation risk is purchasing power risk.
What Are the Main Sources of Market Risk?
Market risk is the danger of losing money as a result of circumstances affecting a whole market or asset class. Because it impacts all asset classes and is unexpected, market risk is also known as undiversifiable risk. Only by hedging a portfolio can an investor reduce this type of risk. The total market is influenced by four key sources of risk: interest rate risk, equity price risk, foreign exchange risk, and commodities risk.
#1. Interest Rates Risk
Interest rate risk is the danger of increasing volatility as interest rates vary. When interest rates move, many forms of risk exposures can occur, including basis risk, options risk, term structure risk, and repricing risk.
Basis risk is a component that arises as a result of potential changes in spreads when interest rates fluctuate. When the spread between interest rates in different markets fluctuates, basis risk occurs.
#2. Equity Price Risk
Equity price risk is the risk that results from securities price volatility — the chance that the value of a security or a portfolio will drop. The risk can be either systematic or ad hoc. Diversification can decrease unsystematic risk, but not systematic risk. Equity price risk is systemic in a global economic crisis since it affects numerous asset classes.
Only by hedging against this risk can a portfolio be protected. For example, if an investor holds numerous assets that reflect an index, the investor might mitigate stock price risk by purchasing put options in the index exchange-traded fund.
#3. Foreign Exchange Risk
Currency risk, often known as foreign exchange risk, is a type of risk that occurs when currency exchange rates fluctuate. Because of poor hedges, global enterprises may be exposed to currency risk when conducting business.
Assume, for example, that a US investor had investments in China. When the two currencies are exchanged, the realized return will be altered. Assume the investor obtains a 50% return on investment in China, but the Chinese yuan falls 20% against the US dollar. Due to currency fluctuations, the investor will only receive a 30% return. Hedging with currency exchange-traded funds can help to lessen this risk.
#4. Commodity Risk
Commodity price risk is the volatility in market price caused by a commodity’s price change. It affects a variety of industry sectors, including airplanes and casino games. Politics, seasonal changes, technology, and current market conditions all have an impact on commodity prices.
Assume there is a surplus of crude oil, causing oil prices to decline every day for the previous six months. Commodity price risk exists for a company that has a significant investment in oil drilling wells. The company’s profit margin will also shrink because it is still operating at the same cost, but crude oil prices are declining. Its profits will fall. To hedge this risk and reduce the uncertainty of oil prices, the corporation could employ futures or options.
Market Risk Premium
The is the rate of return on a risky investment. It is the difference between the expected return and the risk-free rate. It is part of the Capital Asset Pricing Model which we use to work out rates of return on investments. Ideally, an investment gives a high rate of return with low risk, however taking bigger risks can earn bigger rewards.
There are several areas that need to be considered when deciding this. They include:
#1. Historical market risks premium
The return’s past performance is used to determine the premium. This can vary depending on which instrument we use. Generally, the S&P 500 we use as a benchmark for understanding past performance.
#2. Required Market Risk Premium
This is the least rate of return that investors should look for, sometimes known as the hurdle rate of return. If this is too low, investors are unlikely to invest. This will change from investor to investor.
#3. Expected market risk premium
Based on expectations, this will also change depending on the investor.
Other forces can impact it too. For example, the UK calculations may also want to consider economic events like Brexit.
Market Risk Premium Formula
In the capital asset pricing model (CAPM), the market risk premium shows the slope of the security market line (SML). We can derive this formula by subtracting the risk-free rate of return from the expected rate of return.
Mathematically, we can express it as, Market risk premium = Expected rate of return – Risk-free rate of return
or Market risk premium = Market rate of return – Risk-free rate of return

We can derive the formula in the first method by using the following simple four steps:
Step 1: Firstly, find out the expected rate of return for the investors based on their risk appetite. The higher it is, the higher would be the expected rate of return to compensate for the additional risk.
Step 2: Next, determine the risk-free rate of return. This is the return you expect if the investor does not take any risk. The return on government bonds or treasury bills is a good substitute for the risk-free rate of return.
Step 3: Finally, we derive the formula by subtracting the risk-free rate of return from the expected rate of return, as shown above.
We can also derive the formula of the calculation for the second method by using the following simple four steps:
Step 1: Firstly, determine the market rate of return, which is the annual return of a suitable benchmark index. The return on the S&P 500 index is a good proxy for the market rate of return.
Step 2: Next, determine the risk-free rate of return for the investor.
Step 3: Finally, we derive the formula by subtracting the risk-free rate of return from the market rate of return, as shown above.
Also, it can be calculated using a market risk premium calculator
Let’s see some simple to advanced examples of the Formula.
Example #1
An investor who invested in a portfolio and expects a rate of return of 12% from it. In the last year, government bonds have given a return of 4%. Based on the given information, determine the market risks premium for the investor.
Therefore, the calculation can be done as follows,
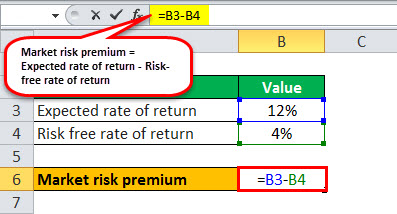
Market Risk premium = 12% – 4%
The result will be-
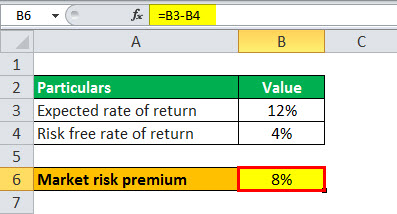
Based on the given information, the market risks premium for the investor is 8%.
Example #2
An analyst wants to calculate the market risks premium offered by the benchmark index X&Y 200. This grew from 780 points to 860 points during the last year. Within this period, the government bonds have given an average 5% return. Based on the given information, determine the market risk premium using the formula.
To calculate this, we will first solve for the Market Rate of Return based on the above-given information.
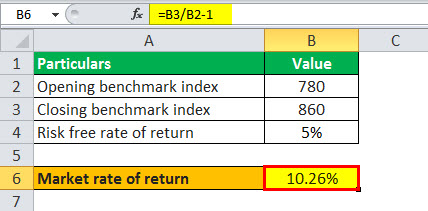
Market rate of return = (860/780 – 1) * 100% = 10.26%
Thus, the calculation can be done as follows,
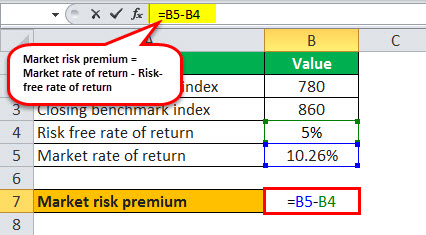
Market risks premium = 10.26% – 5% = 5.26%
A market risks premium calculator is a finance tool used for calculating the market risk premium. You can use the following Market Risk Premium Calculator.
| Expected Rate of Return | |
| Risk Free Rate of Return | |
| Market Risk Premium Formula | |
| Market Risk Premium = | Expected Rate of Return – Risk-Free Rate of Return |
| 0 – 0 = | 0 |
It is important for an analyst or an investor to understand this because it goes around the relationship between risk and reward. It expresses how the returns of an equity market collection differ from that of the lower risk treasury bond yields. This is owing to the additional risk that is borne by the investor. Basically, the risk premium covers expected returns and historical returns. The expected market premium usually differs from one investor to another based on their risk appetite.
On the other hand, the historical market risks premium is the same for all the investors as the value is based on past results. Further, it forms a part of the CAPM, which has already been mentioned above. In the CAPM, the required rate of return of an asset is calculated as the product of market risk premium and beta of the asset plus the risk-free rate of return.
Read also: Financial risk management: All you need to know
Market risks in the banking

This mostly occurs from a bank’s activities in capital markets. It is due to the unpredictability of equity markets, commodity prices, interest rates, and credit spreads. Banks are more exposed if they are heavily involved in investing in capital markets or sales and trading. Market Risks in Banking is the possibility of a loss arising in either the Banking or Trading Book. This is when the values of the assets decrease as a result of increases in interest rates, volatility, and several other factors. If the Bank is short in some assets, then the risk is the increase in asset prices. It is mostly a Trading Book phenomenon.

How to Manage Market risks in Banking
Market risk management involves developing a detailed and powerful structure. This is for monitoring, measuring, and controlling liquidity, interest rate, foreign exchange, and commodity price risks. Market risks management in banking should be combined with the institution’s business plan. In addition, stress testing can assess possible problem areas in a given portfolio.
Other ways to reduce market risks in banking is to include hedging their investments with other, inversely related investments. Commodity prices also play a role because a bank may be invested in companies that produce commodities. As the value of the commodity changes, so does the value of the company and the value of the investment. Changes in commodity prices are caused by supply and demand shifts that are often hard to foretell. So, to decrease this, diversification of investments is important.
Every investment has its ups and downs. Investments involve different levels and types of risk. These risks can be associated with the specific investment, or with the marketplace as a whole. As you build and maintain your business, remember that global events and other factors you cannot control can affect your investments. Be sure to take both business and market risks into account. Although the market rate premium can offer guidance based on past performance, it should not be seen as a way of perfectly predicting future performance.
What are the sources of market risk?
Market risk can come from a variety of sources, including changes in market prices and economic conditions, changes in interest rates, changes in currency exchange rates, changes in commodity prices, changes in credit risk, and changes in liquidity. Market risk can also be influenced by macroeconomic factors, such as inflation, unemployment, and political and social events.
What are the best practices for managing market risk?
The best practices for managing market risk include: diversifying investments, regularly monitoring portfolio performance, adjusting portfolio holdings as needed, using hedging strategies, and staying informed about market conditions and economic trends. It is also important to understand the sources of market risk and to assess the potential impact of market events on investments.
What is the role of diversification in managing market risk?
Diversification is a key tool for managing market risk. By spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions, investors can reduce the impact of market events on their portfolios. This helps to mitigate the effects of market risk and can improve portfolio performance over time.
How does market risk affect the value of financial instruments?
Market risk can have a significant impact on the value of financial instruments, including stocks, bonds, and other securities. Changes in market prices, economic conditions, interest rates, and other factors can cause fluctuations in the value of these instruments. As a result, investors must be aware of market risk and understand how it may affect the value of their investments.
How can market risk affect the stability of the financial system?
Market risk can pose a threat to the stability of the financial system by leading to significant losses for financial institutions and investors. When market conditions change rapidly or unexpectedly, it can cause widespread panic, leading to a decline in confidence and a decline in the value of financial instruments. This can trigger a chain reaction, causing further losses and instability in the financial system.
What is the impact of market risk on business operations?
Market risk can have a significant impact on business operations, particularly for businesses that are heavily dependent on financial markets or that have significant financial exposure to market events. Changes in market conditions can impact the availability of credit, the cost of borrowing, and the value of financial assets. As a result, businesses must be aware of market risk and take steps to manage their exposure to market events in order to protect their operations and financial stability.
Market Risks FAQ’s
How is Market Risk Defined?
Market risk is a measure of all the factors influencing the performance of financial markets. From the standpoint of an investor, it refers to the probability of an investor suffering losses as a result of factors affecting the general performance of the financial markets in which such an investor has placed investments.
How do you determine market risk?
The market risk premium can be computed by subtracting the risk-free rate from the predicted stock market return, providing a quantitative measure of the additional return requested by market participants in exchange for the greater risk.
What is the importance of market risk?
It explains what an investor should and should not buy at any particular time and in any given situation. Every investor is unique, and so is every investor’s risk perception.
What is market risk operational risk?
A type of risk that outlines the hazards that a corporation or firm faces when attempting to operate in a specific field or industry.
What are different types of risks?
There are several types of risk, such as investment risk, market risk, inflation risk, company risk, liquidity risk, and others. Individuals, businesses, and countries all face the danger of losing some or all of their investments.







