In Nigeria, we are blessed with abundant natural resources and yet recognized as the largest economy in Africa. But even with this fact, hustle, and hard work we put in, there are some factors such as healthcare, food insecurity, education, nutrition, and access to cooking fuel, that are highly contributing to the national poverty index in Nigeria. Hence the emergence of the poorest states in Nigeria today.
Interested in knowing what these states are and how they ended up on the list? Then stay with me let’s access the list together.
Key Points
- Nigeria’s poverty is influenced by factors such as healthcare, food insecurity, education, nutrition, and access to cooking fuel.
- 65% of Nigeria’s poor population resides in the northern part of the country, while 35% live in the southern regions.
- Sokoto is the poorest state with a Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) of 91%, largely due to poor infrastructure, education, and healthcare.
- States like Bayelsa, Jigawa, and Gombe also rank among the poorest, struggling with issues such as unemployment, poor agriculture, and geographical challenges.
- Despite these challenges, efforts are being made through government initiatives and development programs to improve conditions in these states.
The Highlights
According to recent research, surveys, and diverse statistics in the country, it was recorded that 65% of the poor people that are in Nigeria stay in the northern part of the country, while the remaining 35% percent of them stay in the Southern part as well.
When it comes to the rural and urban areas, these statistics show that 105.98 million people living in the rural areas are poor, with a multidimensional poverty index of 0.302, while 26.94 million people are poor in urban areas, making it an MPI of 0.155.
To even drive in a deeper depth, 45.49 million population in the Northwest zone are also termed as poor, with an MPI of 0.324, while the South-Eastern region has over 10.85 million poor people and an MPI of 0.183. The Sout-West in this case has the lowest MPI rate at 0.151, followed by South-East and South-South with 0.183 and 0.25 respectively.
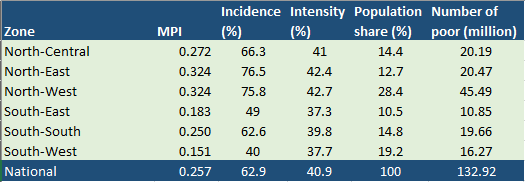
Now coming to the particular causes of these outrageous numbers, you will see that these numbers are backed by some factors. While the problem with the North-West region was mostly nutritional deprivations, the South was more prone to food insecurity. Then we have the South-South region that is mostly disturbed with unemployment and security shocks were the issue of the day in South-South, North Central, and North East.
All these are collective factors that contributed negatively to the economy of these regions in Nigeria. Let’s now move over to getting a hang of these poorest states in Nigeria.
Poorest States in Nigeria 2024

Despite the position of Nigeria in Africa, almost half of the population (40.1%) struggle with poverty. Let’s quickly analyze this list together:
Disclaimer: This guide uses data from the NBS 2022 Multidimensional Poverty Index Report. Poverty rates can change over time, so the information may not fully show the current situation.
#1. Sokoto

Yes. Sokoto is the number one poorest state in the country. It is located in northwestern Nigeria and it has consistently taken up this position for a couple of years. According to the statistics of the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), it was estimated that the MPI for Sokoto state was around 91%, which automatically means that the state lacks in areas like health, education, sanitation, and living standards.
Aside from these factors, one can also link the poverty situation of the state to its rural nature which has limited it to having stable infrastructures and economic possibilities. There has been high interest in agriculture as the only means of survival which has also had its side effects on the population. Education has also been moved down the drain and the rate of unemployment? Nothing to write home about.
However, all hope hasn’t been lost. The Nigerian government has seen to it and has implemented various initiatives in Sokoto. These initiatives range from social safety net programs to agricultural development projects and numerous NGOs work aimed to improve on the factors they are lacking.
#2. Bayelsa
Bayelsa is the second poorest state in Nigeria and its MPI has risen up to 88.5% and they are faced with quite a few challenges. First, there is a large oil exploration and production going on in the state and this has caused them some functions like fishing and farming. They also battle with clean water and sanitation in most of these communities.
In addition to that, there is also a high rate of unemployment in Bayelsa and it has hindered many opportunities in the oil sector as well.
However, there have been tremendous efforts to rectify the current situation in Bayelsa state. Some initiatives like skill development can help the population in the long run and also get them into the oil industry.
#3. Jigawa
Jigawa is also termed one of the poorest states in Nigeria and the MPI rate was around 84.3% according to the last statistical report from the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). The state has been faced with important necessities like healthcare, education, and sanitation.
They specialize mostly in agricultural farming but with the inefficient and unavailable modern farming techniques and irrigation systems, they most times face restrictions that end up causing a lack of income.
Education on the other hand isn’t that smooth. There are low literacy rates, especially in the rural areas of the state. And because it has become a norm and almost everyone does not have the luxury of quality education, they end up in a cycle of poverty.
To help alleviate some of these issues, there have also been some improvements in boosting the agricultural sector of the state through improved techniques and infrastructure.
#4. Gombe

This state is also among the list of poorest states in Nigeria with an MPI rate as high as 86.2%. The state ended up in this category mainly because of its geography. Gombe is situated in a very dry and hot land making it difficult to grow crops in the land. And even when it rains, the farmers have to struggle harder to make enough food for their families and the community at large.
Aside from the farming discomfort, the state is also situated in an outskirt area far from major cities and trade routes, making it difficult for them to transport goods in and out of the state. What is a state without transportation? It will even go as far as limiting any form of investment from other states because of the stress of transportation.
#5. Plateau
Most of the states I have listed so far are in the northern part of Nigeria if not all. Plateau is also on the list as one of the poorest states in Nigeria with a Multidimensional Poverty Index rate at around 84%. This state has most of its problems coming from the height of violence and insecurity in the vicinity for some years now.
The violence in question is so depth that it disrupts normal economic activity, damages infrastructure, and discourages investment. Imagine when investors are afraid to invest and help advance some sectors of the state, it will be nothing to write home about. No opportunities and fewer jobs will be the order of the day thereby enforcing more violence in the state.
They also have issues with the agricultural aspect of the state which is mainly caused by the lack of rain experienced in the state. In addition to that, they are faced with serious Inadequate infrastructure development which slows down the economy of the state.
#6. Kebbi
One of the poorest states In Nigeria is Kebbi State with a multidimensional poverty rate of around 83.5%. While some issues we examined in other states were lack of water and inability of the crops to grow, the case with Kebbi is it has an abundance of water. The mighty Niger River weaves through its heart and the ugly side of this is that the state falls within the Sudan Savannah, represented by hot temperatures and seasonal flooding.
Due to the flooding, agriculture is almost impossible in this state. Whenever the flood comes it destroys crops and displaces families, disrupting livelihoods and pushing people into poverty.
Even despite the presence of the Niger River, irrigation systems haven’t reached their full potential across Kebbi. At least with irrigation being present, it controls water flow and ensures a steady supply for agriculture throughout the year. But they don’t have that luxury.
#7. Zamfara
In Zamfara, they have a poverty rate of around 82% and in addition to that, they also struggle with insecurity at its highest order. In Zamfara unlike Plateau, it takes different forms including cattle rustling, banditry, kidnapping, and more. This has posed a threat and also discouraged trading and access to markets.
Everyone is scared of working or even leaving their house including farmers and that has affected their agriculture a lot. Also, insecurity discourages investment.
Businesses are reluctant to invest in areas with a high risk of violence, limiting job creation and economic growth.
#8. Ebonyi
Ebonyi state is blessed with good and fertile land, but even at that they still face poverty, and the rates were about 81%. But since their issue is not based on land, it must be linked to something, and it’s no other than infrastructure.

Farmers use their good lands to cultivate something nice but to take it to other cities and states becomes a nightmare. they face poor roads, unreliable electricity, and inadequate irrigation systems. And these are mostly what they use to increase profit margins and expand production but they can’t anymore. To break this cycle, Adamawa needs to invest in a variety of economies.
#9. Adamawa
With its 80% MPI poverty rate, this state has been facing hardship due to a lack of diversification. They are based mostly on agriculture and if anything should happen to a crop, they will starve. Again, limited job opportunities outside of agriculture restrict income sources and delay overall economic growth.
To break this cycle, Adamawa needs to invest in a variety of economies. if this is handled, it can improve the economy and still attract investors and tourists to the state.
#10. Katsina
Katsina State is also struggling with poverty despite having hardworking residents. According to the study, one key reason is that there’s limited access to education and skill development opportunities In the state.
However, breaking this cycle requires investment in education and skill development programs. This could involve providing scholarships, establishing vocational training centers, or offering courses in new technologies relevant to the job market.
Which is the Richest State in Nigeria?
Just as much as we have the poorest states available in Nigeria, we also have the richest of them as well. Lagos is one of the richest states in Nigeria with a GDP of $33.68 billion and an annual budget of $4.2 billion. It is also known to be one of the oldest states in Nigeria and has been in existence since 1967. Its progress is mostly attributed to the rapid growth and development of the state including its high population.
Here is a list of the top poorest states in Nigeria for easy assessment:
Poorest States in Nigeria Checklist.PDF
Conclusion
If you have always pondered on what the poorest states in Nigeria could be, then this guide has all the information you need on that and more. Here I have listed a detailed list of the poorest states in Nigeria while stating why it is so. While these states being poor still doesn’t limit them from having unique cultural, historical, and economic aspects, they just need a little push to help alleviate their status.
- FINANCIAL INCLUSION: Overview, Importance, Objectives, Examples (+ Free PDFs)
- 15 Must-Read Real Estate Investing Books for Beginners
- How To Invest in Real Estate in Nigeria: Tips You Need






